The Internet of Things (IoT) has become crucial for accurate air quality monitoring systems, as it enables the use of real-time and historical data to support business operations. Through air quality IoT integration, you’ll access key insights to improve air quality management, protect human health, and build smarter cities.
Why Air Quality Data IoT Integration Matters
Monitoring air quality in cities, workplaces, and homes has become an essential element of protecting public health and tracking the progress of regulatory compliance on environmental conditions. While the Clean Air Act, passed in the 1970s, has significantly reduced pollution, there is still a long way to go.
The Environmental Protection Agency notes that in 2023, 66 million tons of pollution were emitted into the atmosphere in the United States. These emissions come from factories, vehicles, and even food production.
Policy changes regarding pollution have a profound real-world impact. Tightened EPA regulations could prevent over 4,500 premature deaths per year by 2032 by reducing health problems like asthma, heart disease, and cancer.
Modern technology has provided us with ways to monitor these changes and make informed decisions about how to move forward. IoT systems, such as air quality sensors, provide hyper-local, granular data, enabling faster and more informed decisions.
IoT sensor data can be easily connected to an API like Visual Crossing, which allows users to combine forecasts and indoor air quality information. This improves the predictive power of air quality monitoring, as weather systems can significantly impact air pollution.
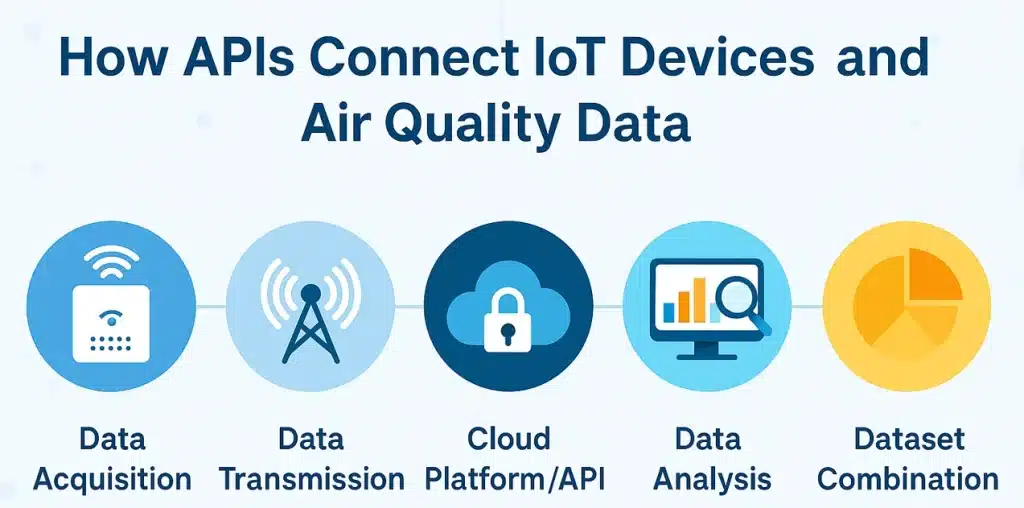
How APIs Connect IoT Devices and Air Quality Data
APIs are the bridge between IoT sensors and environmental monitoring platforms. Here’s a simple overview of how this process works.
- Data Acquisition: First, the sensor collects data on the environment. This can be achieved through various methods, including measuring chemical reactions, utilizing ultraviolet light to break down ozone molecules, or employing lasers to track particulate matter.
- Data Transmission: After data collection, the sensor will transmit this information to a cloud-based platform or server using an API. The API provides the sensor with a key, which “unlocks” access to the platform. This may be done through WiFi, Bluetooth, or cell towers, depending on the specific device.
- Data Processing and Analysis: The data is cleaned and formatted. Algorithms will combine the different datasets for specific pollutants to determine an air quality index (AQI) number, such as 53.
- Dataset Combination with Other Environmental Monitoring Tools: With APIs like Visual Crossing, data can be combined with other datasets, such as temperature, precipitation, and humidity, to gain a more comprehensive understanding of current conditions. This information is collected from other types of sensors, often from high-quality government resources like the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA).
- Client Applications: A user can then request access to this dataset using their API key. Using a secure protocol, the data is integrated into the user’s application, such as a custom weather dashboard for their business or an AI platform for policymakers.
While this may seem like a laborious process, data collection and transmission occur in real-time, with only minutes separating the sensor’s submission of the data and the user’s receipt of the information. Algorithms can crunch thousands of calculations almost instantaneously.
Air Pollution Using IoT Devices
Air pollution is composed of various gases, including volatile organic compounds (VOCs), carbon monoxide, particulate matter (PM2.5 and PM10), carbon dioxide, ozone, and other pollutants such as benzene. There are several methods for collecting this information, and most sensors employ a combination of them.
- Gas Sensors: Electrochemical sensors measure changes in conductivity or voltage across the sensor, which track gases such as carbon dioxide or nitrogen dioxide.
- Optical Sensors: Ozone sensors utilize ultraviolet light to break down ozone molecules. Through this, it can identify the overall concentration of the gas.
- Particle Sensors: A laser-based sensor emits a beam of light through the air and measures how it scatters, allowing for the detection of PM2.5 and PM10.
- Heat Sensors: This assesses the temperature and humidity, which significantly impacts air quality.
Each of these different metrics is transmitted to the server in standards like µg/m3 or parts per million (ppm). The server receives the raw data from each sensor, calculates averages, and combines the various measures to create the air quality index, presenting the information in a more user-friendly format. AQI is color-coded to give individuals a simple, easy-to-understand idea of whether the air is safe or highly polluted.
Companies and policymakers can measure air pollution using IoT devices, which will detect the gas concentrations and transmit this information to an API. IoT solutions, when strategically placed throughout urban areas, can create detailed pollution maps and unlock key insights for air quality management.

Real-Time Monitoring with IoT and APIs
Real-time air quality monitoring allows immediate responses to emerging threats, such as wildfire smoke or increased carbon emissions when roads are congested. This enables municipalities, companies, and individuals to utilize their resources effectively.
For example, an IoT system, such as a smart air filter, may utilize sensors to trigger alerts when PM levels are high. This will let the business owner know that they may need to change their HVAC filters or shut off air intake.
The Role of Environmental Monitoring Systems
Integrating IoT air quality sensors with environmental monitoring systems centralizes vast amounts of data, which improves decision-making. Combining these with APIs provides faster data acquisition and processing, making each system more reliable than it could be on its own.
Using Air Quality Research Data for IoT Insights
One of the benefits of IoT air monitoring is that it can collect data over extended periods of time, all with low power consumption. This can then be combined with other air quality research data, like historical records, to create a more comprehensive picture of the local environment and the factors that impact air pollution.
Weather APIs and Air Quality Monitoring IoT
Environmental conditions have a significant impact on air pollution. During periods of high humidity, heavier pollutants, such as particulate matter, are trapped and amplified. High temperatures increase the reactivity of certain pollutants, such as ozone, and trigger chain reactions that significantly impact air quality.
Gases like sulfur dioxide or nitrogen oxides can become major dangers when combined with precipitation. These are two of the driving forces behind acid rain, which acidifies the soil and damages crops.
Wind is also a key element of air pollution patterns. On humid days with little wind, the pollution cannot disperse and becomes concentrated in certain areas, which increases the risk of respiratory problems for the population.
A weather API seamlessly integrates with air quality monitoring systems to offer a more advanced understanding of pollutants. By tracking both of these components together, organizations see the big picture of these interconnected systems and can more easily predict potential damage.
Enhancing Monitoring with Weather Data
Combining IoT data with weather data supports a more proactive approach to managing air quality. Air pollution does not occur in a vacuum; it is deeply interrelated with weather systems, which can remedy or amplify its effects.
Through an API, users can combine information from air quality monitoring systems and the local weather report to anticipate pollution spikes, which helps them manage risks in advance.
Air Quality Forecasts and Predictive Planning
An air quality forecast, when combined with real-time data from IoT sensors, provides policymakers and businesses with the key insights they need to protect human health and improve their operations.
Suppose a certain region has high nitrous oxide and volatile organic compound emissions because there is a highway that runs through the city, which is used by long-haul truckers. NO and VOCs, when combined with sunlight, produce ozone, which can cause smog and lead to respiratory issues.
Urban planners can identify the “perfect storm” that produces high ozone levels: hot, sunny days with minimal wind and high humidity. When these weather conditions are forecast, they can implement air quality management protocols like rerouting trucks away from the city, running more buses and trains, and encouraging people to stay indoors.
In turn, businesses can work in collaboration with urban planners to reduce air pollution for everyone, all in real time. Logistics companies may agree to use other methods, while bus companies could boost their staffing to discourage people from driving. Together, this ensures healthier and safer urban centers.
Building Smarter Systems with a Weather Query Builder
A weather query builder customizes environmental queries using air quality sensors. IoT users can refine their searches using various parameters, such as the following.
- Air Quality Monitoring by Specific Pollutants: Each pollutant has different health effects. For example, carbon monoxide can cause neurological symptoms, while particulate matter can result in asthma. Additionally, each one has different sources, like car exhaust or factories. Drilling down into the data can help policymakers manage specific pollutants.
- Air Quality by Time: Whether that’s time of day or time of year, air quality changes over time. Certain pollutants are more common in the summer, when temperatures rise and accelerate chemical reactions. Monitoring pollution levels when they spike can improve air quality management and protect health.
- Locations: If a specific area consistently has lower air quality than neighboring areas, users can explore the data to understand the reasons. This can also help troubleshoot problems with particular sensors, which may need calibration or replacement.
Key Benefits of Air Quality Data IoT Integration
Integrating IoT air quality data has numerous benefits, both for individual users and for the community as a whole. These are only a handful of ways that air quality data IoT integration can improve well-being and drive more precise decision-making.
- More Accuracy: Local air quality requires local sensors. By integrating dozens, hundreds, or even thousands of air monitors, users can get a more accurate picture of current air conditions.
- Automation: By utilizing IoT devices with APIs, users can create scripts that automate their applications or devices. A sudden spike in pollution may prompt actions such as shutting off air conditioners, encouraging users to change filters, or closing windows to improve indoor air quality.
- Early Warnings: Combining air quality information with weather forecasting enables users to anticipate potential issues before they arise. They can then take preventative steps to protect their health or reduce pollution.
- Smarter Environmental Strategies: Accurate local data is essential for improving environmental health. Knowing where pollution originates, how it spreads, and what protective measures are already in place enables more precise interventions.
Future Trends in Air Quality IoT and API Integration
Air quality technology continues to improve, ensuring faster performance and deeper analysis of key pollutants.
One of the most exciting innovations is machine learning, which can analyze thousands of data points in a fraction of the time that it would take a human. These systems can consume a vast amount of data, apply physics models, and identify trends. This enables data-driven decision-making, whether that’s determining where to put new public transportation hubs or planning more eco-friendly urban centers.
Satellite integrations can help researchers see how the climate impacts local conditions, which can lead to more effective policy. Regions can collaborate on preventive measures, such as advancing public transportation, while using data to support their suggestions.
Lastly, IoT products are increasingly being adopted by consumers, particularly citizen scientists who are concerned with their own well-being. As these products become more affordable and widespread, users can connect their own devices to APIs and get hyper-local, actionable feedback.
Air quality monitoring is becoming increasingly accurate, accessible, and affordable, benefiting both individuals and businesses. The future of air quality is likely to involve smaller devices strategically placed throughout homes and communities, with data analyzed by algorithms and AI.
Conclusion: Smarter Environmental Monitoring Through IoT and APIs
By combining APIs and IoT systems, organizations can develop a comprehensive solution for ensuring clean air in urban environments. Air quality data IoT integration is a convenient, low-cost, and long-term solution that will only strengthen as Big Data grows more refined.
Visual Crossing is a lightweight, flexible, yet robust API that integrates easily with a variety of products, including IoT air monitors. With numerous specialized datasets and a generous free request limit, it is accessible for a broad range of users, from individuals to enterprise companies. Advance your decision-making and get the most out of your air quality sensors through Visual Crossing’s API.

